What is a Virtual Reality Tour?
A virtual reality tour is a digital simulation of an existing location or environment that users can navigate through using a VR headset. This type of tour incorporates 360-degree images or LiDAR scans, that provide a fully immersive experience for the user.
The images are captured using specialized cameras that capture images in every direction, allowing the user to feel as though they are physically present in the location.
Users can move around in the virtual environment by using a handheld controller or keyboard and mouse, or even by physically moving their bodies.
VR tours allow users to visit remote locations, interact with future-planned cityscapes, or even travel into the past to compare how today’s archeological ruins looked thousands of years ago.
Virtual reality tours are most commonly used in real estate, architecture, and tourism industries, where they offer a cost-effective and efficient way to showcase properties and locations to potential buyers or visitors.
We’re most excited to offer this technology because virtual reality tours provide a unique and engaging way for users to experience a location without having to physically be there, enabling a wide range of experiences.
How Virtual Reality Tours are Made
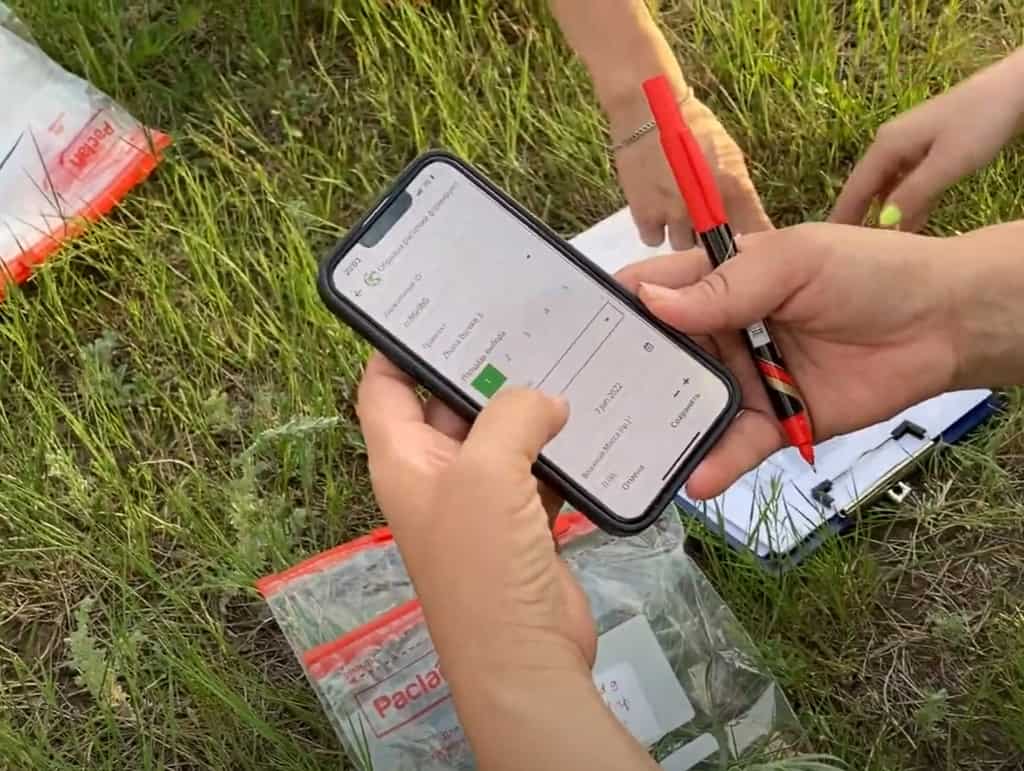
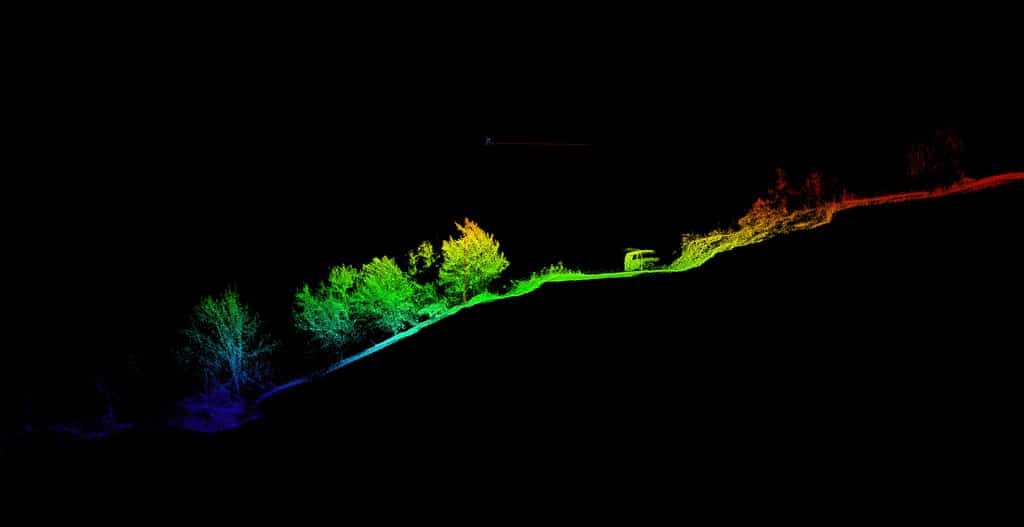
Virtual reality tours typically start with the capture of visual data from the environment being simulated. This can be done using a variety of methods, including 360-degree cameras, LiDAR scanners, or photogrammetry.
360-degree cameras take images from every direction, which are then stitched together to create a seamless panoramic image. LiDAR scanners use lasers to capture precise measurements of the environment, which can be used to create an accurate 3D model. Photogrammetry involves taking multiple photographs of an object or environment from different angles, which are then used to create a 3D model by analyzing the differences between each photograph.
rTek also uses 360-degree video to make immersive environments, including audio and live action, allowing users to gain a fuller sensory experience of the real location.
What is Mixed Reality?
rTek combines reality capture (a high-fidelity representation of objects in the real world) with other objects to create a mixed reality. For example, you can blend two different times or seasons to view a before/after scene. Or, you can blend a real place with the planned 3D model of new construction. You can even add virtual tags linked to videos or other 2D media located anywhere in the 3D space, providing users with more context, interactivity, and storytelling capabilities.
Once the visual data has been captured, it is processed and optimized for use in a virtual reality environment. This typically involves reducing the size and complexity of the data to ensure that it can be rendered in real-time on VR hardware. The data is also often optimized to ensure that it can be downloaded quickly and easily by users.
Once the visual data has been processed, it is imported into virtual reality software to create the virtual environment. The VR software allows rTek to create interactive elements within the environment, such as hotspots that provide additional information or interactive objects that users can manipulate.
Interactivity is virtually unlimited.
rTek’s virtual reality software allows the embedding of videos, animations, avatars, environmental audio, and even games or scoring systems. We can connect to live data as well, and display maps, websites, and streams to augment the virtual environment.
Finally, the virtual reality tour is tested to ensure that it runs smoothly and provides a seamless user experience. This often involves testing the tour on a variety of VR hardware to ensure that it works on different platforms, servers, or websites.
Overall, the process of creating a virtual reality tour requires a combination of technical expertise, creativity, and attention to detail. The resulting tour provides a unique and engaging way for users to experience a location without physically being there, opening up a wide range of possibilities for education, entertainment, and exploration.
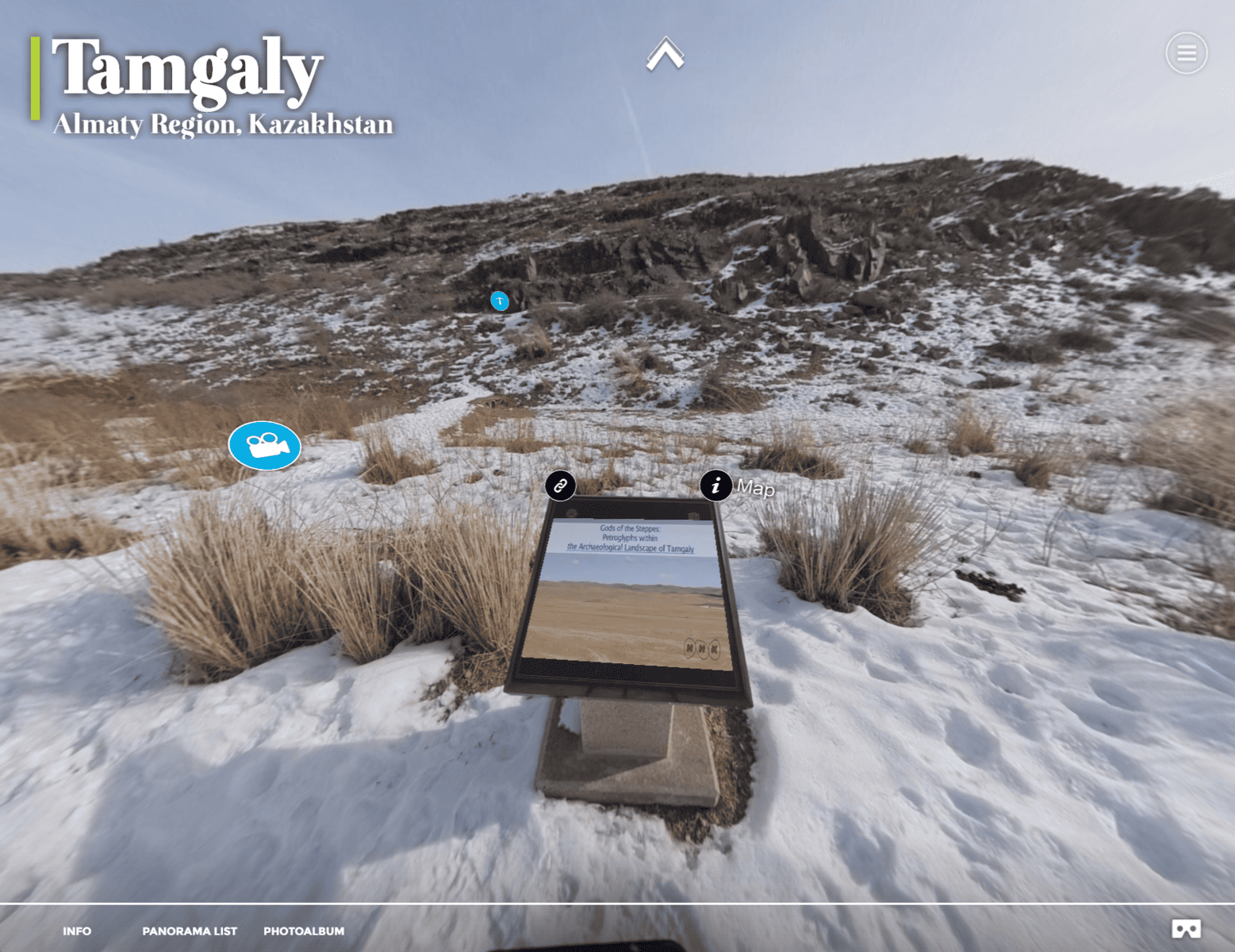
Tamgaly UNESCO Site
Tamgaly is a UNESCO World Heritage site located in Kazakhstan. The site contains a series of rock carvings that date back to the Bronze Age. The carvings depict a variety of scenes, including hunting, dancing, and ritual ceremonies. The site is considered to be one of the most important examples of prehistoric rock art in Central Asia.
The Tamgaly site was first discovered in 1957 by an archaeological team led by A.G. Maksimova. The site was later studied by a number of archaeologists and scholars, who worked to document and preserve the carvings. In 2004, the site was designated as a UNESCO World Heritage site in recognition of its cultural significance.
Recently, the site has been the subject of a reality capture project, which aims to create a digital replica of the site that can be explored using virtual reality technology. The project’s pilot has been carried out by rTek. The resulting virtual reality tour provides a unique and immersive way for people to experience the Tamgaly site, even if they are unable to visit it in person.
A Focus on Preservation
Human activity can damage UNESCO sites like Tamgaly through physical degradation, pollution, and overuse. When people visit sites in person, they often leave behind trash, wear down paths and structures, and disturb the natural environment. This can lead to irreversible damage to the site and its cultural significance.
Virtual visits can help reduce the impact of human activity on sensitive sites like Tamgaly. By exploring the site virtually, people can still experience its cultural and historical significance without causing physical damage. Additionally, virtual visits can help increase accessibility to UNESCO sites for people who may not be able to travel to the area in person. This can lead to increased awareness and appreciation of these sites, and can ultimately lead to increased efforts to protect and preserve them for future generations.
The Future of Virtual Reality Tours
Virtual reality tours have the potential to become even more immersive and interactive in the future. For example, they could incorporate 3D models of heritage sites that show what they looked like in the past, creating a time-lapse effect that allows visitors to see how the site has changed over time. Additionally, virtual reality tours could include interviews with experts or local guides, providing visitors with a more in-depth understanding of the site’s cultural and historical significance.
Another possibility is the use of augmented reality, which could allow visitors to interact with the environment in new and exciting ways. For example, visitors could use their devices to overlay additional information about the site onto their view, such as historical facts or stories about the people who lived there.
Virtual tour guides could also become more common, providing visitors with a more personalized experience and helping them navigate the site more easily. This could help to make the experience of visiting a heritage site more accessible and engaging for a wider range of people.
Overall, the future of virtual reality tours is bright, with many exciting possibilities for enhancing the visitor experience and promoting the preservation of cultural heritage sites.